Flange
- Flanges General
- Flanges are used to connect valves, pipes, pumps and other equipment to make a pipework system. Typically flanges are welded or threaded, and two flanges are connected together by bolting them with gaskets to provide a seal that provides easy access to the piping system. These Flanges are available in various types such as slip on flanges, weld neck flanges, blind flanges, and socket weld flanges, etc. Below we have explained the various types of flanges used in the piping systems depends on their sizes other factors.

-
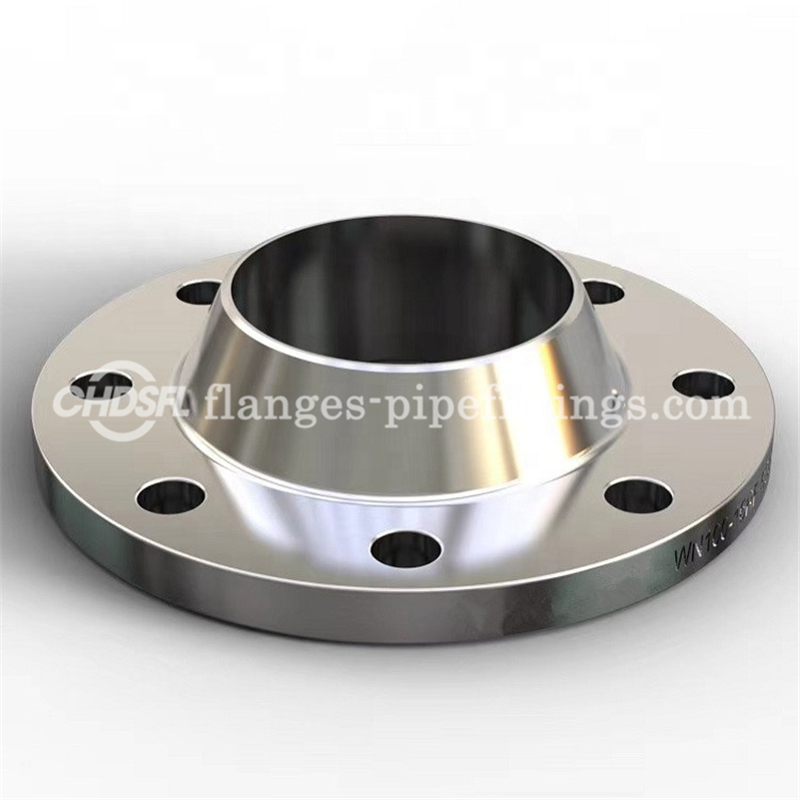
Oem Manufacturers Custom Stainless Steel Dual Grade 316/316L Weld Neck Flange WNRF
Welding Neck Flanges are easy to recognize as the long tapered hub, that goes gradually over to the wall thickness from a pipe or fitting. The long tapered hub provides an important reinforcement for use in several applications involving high pressure, sub-zero and / or elevated temperatures. The smooth transition from flange thickness to pipe or fitting wall thickness effected by the taper is extremely beneficial, under conditions of repeated bending, caused by line expansion or other variable forces.These flanges are bored to match the inside diameter of the mating pipe or fitting so there will be no restriction of product flow. This prevents turbulence at the joint and reduces erosion. They also provide excellent stress distribution through the tapered hub.The Weld neck flanges are attached by butt-welding to the pipes. These are used mainly for critical services where all the weld joints need radiographic inspection. While specifying these flanges, the thickness of the welding end also should be specified along with flange specification.

-
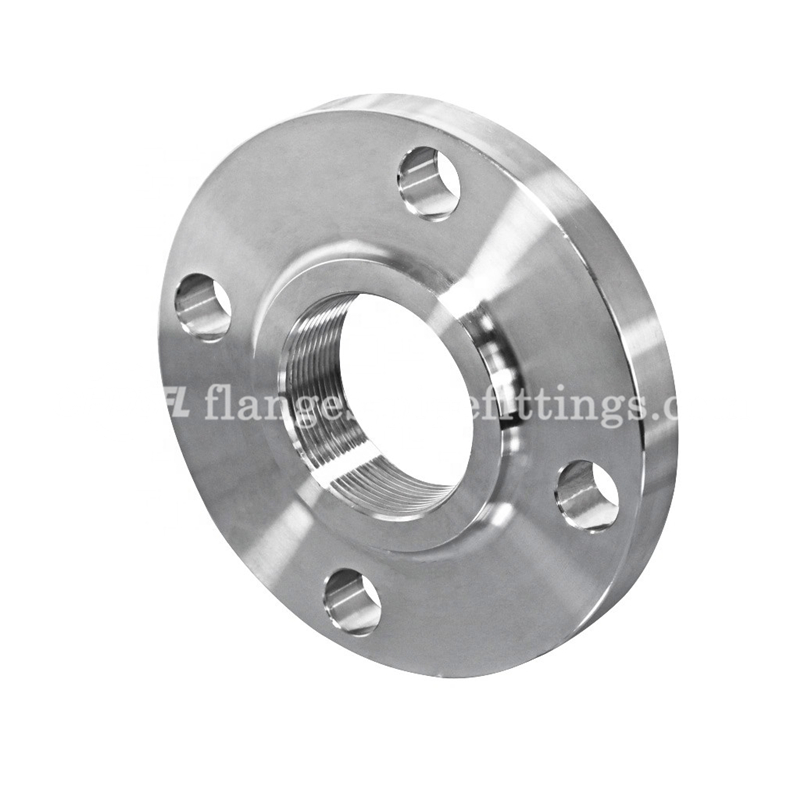
Quality Assurance Stainless Steel For Industrial From China Female Threaded Flange 3 Inch Pipe Flange 8 Holes Flange
Threaded flange is also called screwed flange or screwed-on flange.this style has a thread inside the flange bore which fits with the matching male thread on the pipe or fitting. This type of flange is used where welding is not an option. Threaded flange is most commonly used on low pressure applications and smaller pipes (up to 4″ nominal).

-
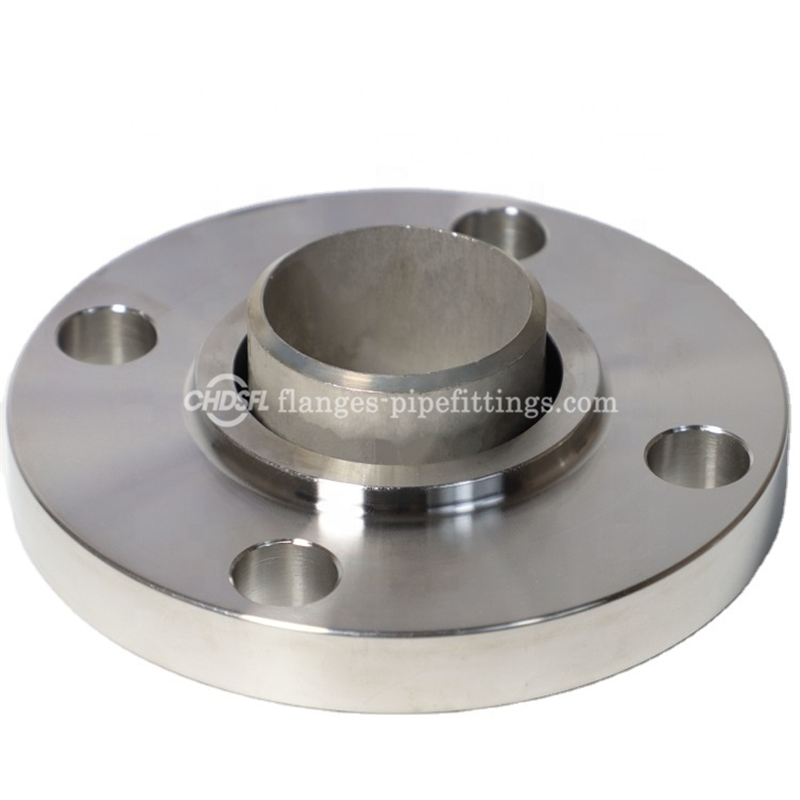
Stainless Steel EN1092-1 TYPE 2 LOOSE PLATE flange
This type of flange consists of both a stub end and a flange.The flange itself is not welded but rather the stub end is inserted / slips over the flange and is welded to pipe. This arrangement helps in flange alignment in conditions where non-alignment may be an issue. In a lap joint flange, the flange itself is not in contact with the fluid. The stub end is the piece which gets welded to the pipe and is in contact with the fluid. Stub ends comes in type A and type B. Type A stub ends are most common. Lap joint flange only comes in flat face. People confuse lap joint flange with slip on flange as they look very similar with the exception that lap joint flange has round eges on the back side and a flat face.

-
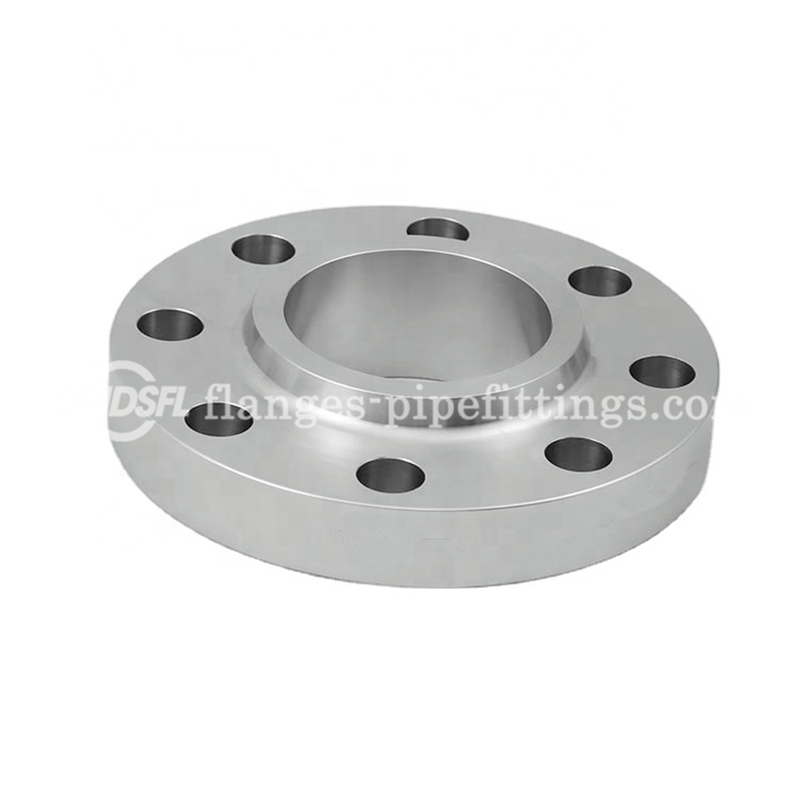
JIS B2220 Standard Pipe Fitting Flange 304 Stainless Steel Slip On Flange
Slip on Flange Is fundamentally a ring placed over the end of the pipe, with a flange face extending from the end of the pipe by sufficient distance to apply a welded bead to the inner diameter. As the name suggests these flanges slip over a pipe and hence known as Slip On Flanges. A slip-on flange is also known as SO flange. It’s a kind of flange that are slightly bigger than the pipe and slides over the pipe, with internal design. Since the inner dimension of the flange is slightly bigger than the external dimension of the pipe, the top and bottom of the flange can be connected directly to equipment or pipe by fillet welding the SO flange. It is used to insert the pipe into the flange’s inner hole. Slip-on pipe flanges are used with a raised or flat face. Slip-On Flanges are a suitable choice for low-pressure applications. Slip on flange is excessively utilized in many fluid pipelines.

-
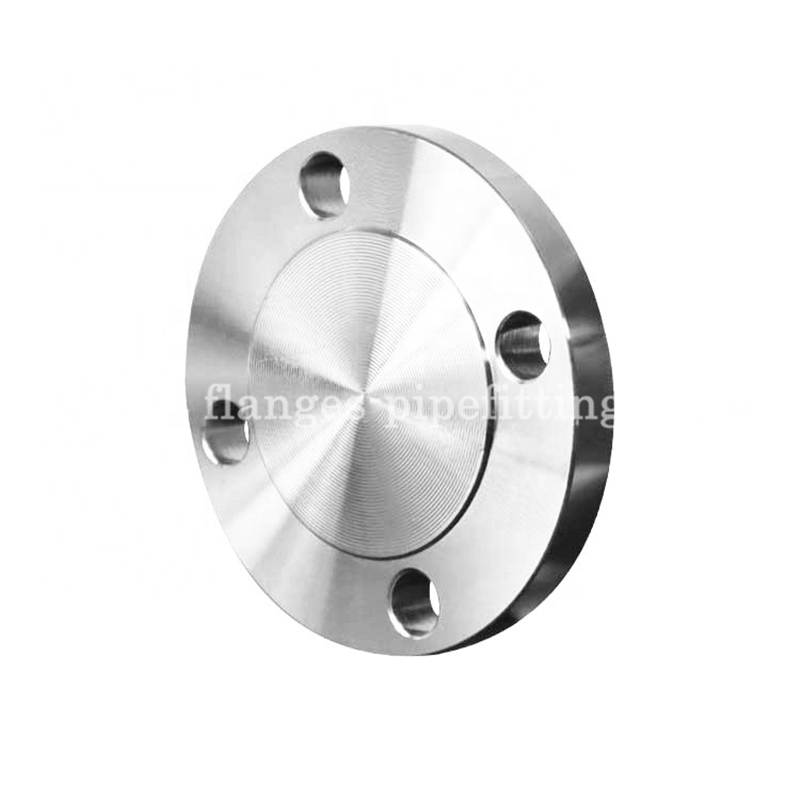
ASTM 316/316L Blind Flange/pipe Fitting ANSI B16.5 CL600 Forged Flanges Stainless Steel BLD Flange
Used for terminating or isolating piping systems, blind flanges are essentially boltable blank discs. When installed properly and combined with the correct gaskets, they can achieve an outstanding seal which is easy to remove when needed.

-
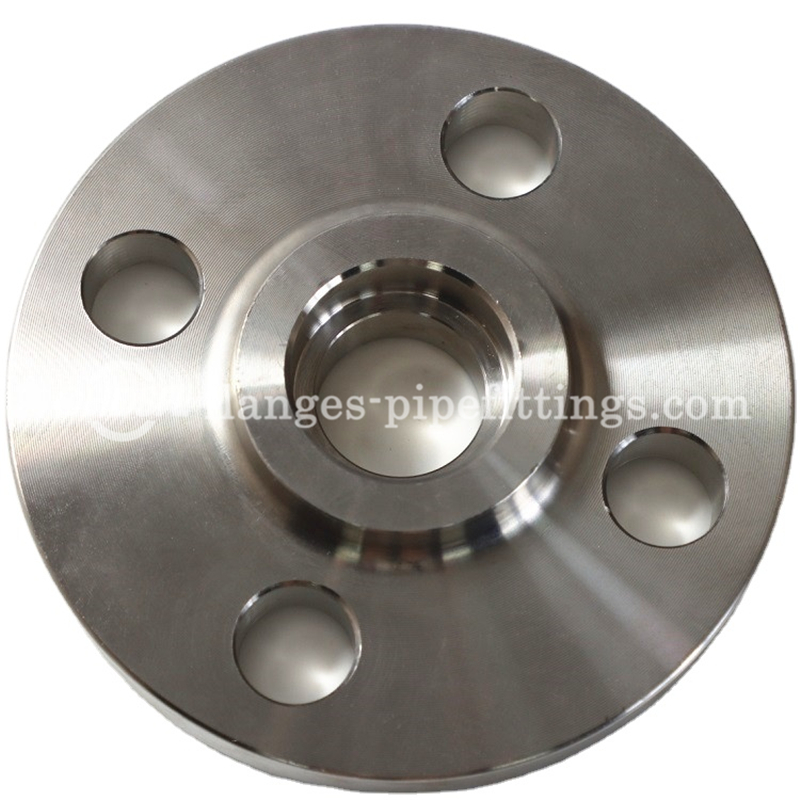
ANSI DIN EN BS JIS ISO Forged Steel Socket Weld Flange For Oil Gas Pipeline
Ideal for smaller pipe diameters in low-temperature and low-pressure scenarios, socket-weld flanges feature a connection in which you place the pipe into the flange and then secure the connection with a single multi-pass fillet weld. This makes this style simpler to install than other welded flange types while avoiding the limitations associated with threaded ends.

- Making The Connection: Flange Facing Types
- Flange face provides a mean to mate the flange with sealing element, usually a gasket. Even though there are many face types, most common flange face types are following;
- Facing types determine both the gaskets needed to install the flange and characteristics related to the seal created.
- Common face types include:
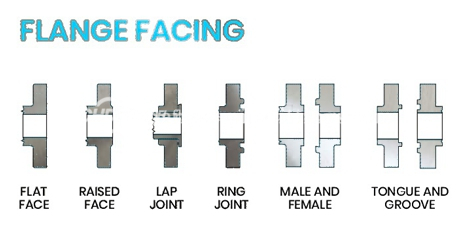
- --Flat Face (FF): As the name suggests, flat face flanges feature a flat, even surface combined with a full face gasket that contacts most of the flange surface.
- --Raised Face (RF): These flanges feature a small raised section around the bore with an inside bore circle gasket.
- --Ring Joint Face (RTJ): Used in high-pressure and high-temperature processes, this face type features a groove in which a metal gasket sits to maintain the seal.
- --Tongue and Groove (T&G): These flanges feature matching grooves and raised sections. This aids in installation as the design helps the flanges to self-align and provides a reservoir for gasket adhesive.
- --Male & Female (M&F): Similar to tongue and groove flanges, these flanges use a matching pair of grooves and raised sections to secure the gasket. However, unlike tongue and groove flanges, these retain the gasket on the female face, providing more accurate placement and increased gasket material options.
- Many face types also offer one of two finishes: serrated or smooth.
- Choosing between the options is important as they will determine the optimal gasket for a reliable seal.
- In general, smooth faces work best with metallic gaskets while serrated faces help to create stronger seals with soft material gaskets.
- The Proper Fit: A Look At Flange Dimensions
- Apart from the functional design of a flange, flange dimensions are the most likely factor to impact flange choices when designing, maintaining, or updating a piping system.
- Common considerations include:
- The dimensions of flanges includes many referenced data, flange thickness, OD, ID, PCD, bolt hole, hub height, hub thickness, sealing face. So it is necessary to confirm the flange dimensions before confirming a flange order . According to different application and standard, the dimensions are different . If the flanges will be used in a ASME standard piping system, the flanges usually are ASME B16.5 or B16.47 standard flanges, not EN 1092 standard flanges.
- So if you place a order to a flange manufacturer , you should specify the Flange dimensions standard and material standard .
- The link below provides flange dimensions for 150#, 300# and 600# flanges.
- Pipe Flange Dimension Table
- Flange Classification & Service Ratings
- Each of the above characteristics will have an influence on how the flange performs across a range of processes and environments.
- Flanges are often classified based on their ability to withstand temperatures and pressures.
- This is designated using a number and either the “#”, “lb”, or “class” suffix. These suffixes are interchangeable but will differ based on the region or vendor.
- Common classifications include:
- --150#
- --300#
- --600#
- --900#
- --1500#
- --2500#
- Exact pressure and temperature tolerances will vary by materials used, flange design, and flange size. The only constant is that in all cases, pressure ratings decrease as temperatures rise.






